The digital landscape is undergoing a fundamental transformation. Web 2.0 brought us social media, cloud computing, and mobile apps. However, Web3 promises something far more revolutionary: a decentralized internet where users control their data, transactions occur without intermediaries, and businesses operate on transparent, trustless systems. At the heart of this transformation are decentralized applications, or dApps, which are reshaping how we think about digital business.
Understanding the Web3 Revolution
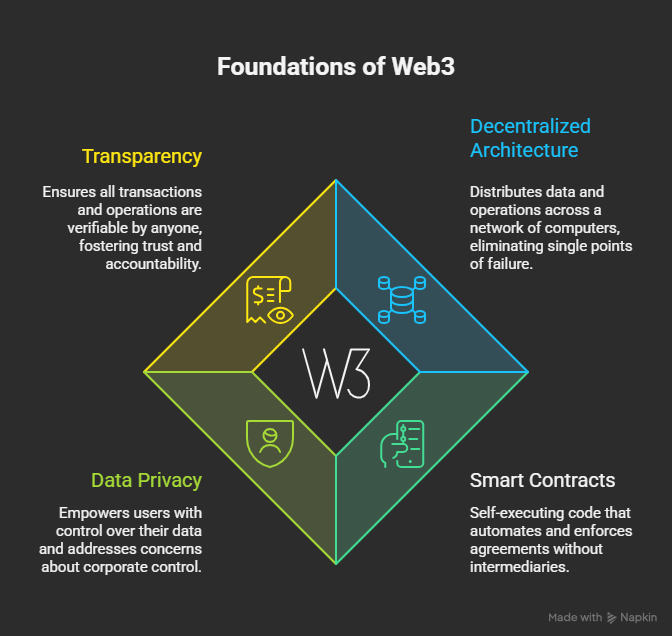
Web3 represents the third generation of internet services, built on blockchain technology and powered by decentralized networks. Traditional web applications rely on centralized servers and databases that single entities control. In contrast, Web3 applications distribute data and operations across a network of computers. This fundamental shift in architecture creates new possibilities for businesses and users alike.
Decentralized applications are software programs that run on blockchain networks rather than centralized servers. Smart contracts power these applications—self-executing code that automatically enforces agreement terms without requiring intermediaries. Consequently, this automation reduces costs, eliminates single points of failure, and creates transparent systems where anyone can verify all transactions and operations.
The rise of Web3 isn’t just a technical evolution. Rather, it’s a response to growing concerns about data privacy, corporate control over digital infrastructure, and the lack of transparency in traditional systems. Users increasingly recognize that their data has value and want more control over how companies use it. Meanwhile, businesses discover that decentralized systems can reduce operational costs while opening new revenue streams.
The Business Case for dApp Development
Traditional digital businesses face several persistent challenges that Web3 dApps can address effectively. Centralized systems require significant infrastructure investment and ongoing maintenance costs. Furthermore, they create single points of failure that hackers can exploit or technical issues can disrupt. They also depend on intermediaries for critical functions like payment processing, identity verification, and data storage. Each intermediary takes a cut of revenue and adds complexity to operations.
Decentralized applications eliminate many of these pain points. By distributing operations across a blockchain network, dApps achieve remarkable resilience. There’s no single server to attack or shut down. Therefore, they become inherently more secure and resistant to censorship. Smart contracts automate processes that traditionally required human oversight or third-party services. As a result, this reduces both costs and the potential for errors or fraud.
The financial implications are substantial. Payment processing through traditional systems involves multiple intermediaries. Each charges fees that can range from two to five percent or more. Additionally, cross-border transactions prove even more expensive and often take days to settle. Web3 dApps process payments directly between parties using cryptocurrency. They charge minimal fees and provide near-instant settlement times. For businesses operating globally, this efficiency gain alone justifies exploring Web3 development.
Beyond cost savings, dApps enable entirely new business models. Tokenization allows businesses to create digital assets representing ownership, access rights, or value within their ecosystem. Companies can trade, stake, or use these tokens as governance mechanisms. This creates dynamic economies around products and services. Non-fungible tokens have demonstrated how businesses can verify and transfer digital ownership. Consequently, this opens possibilities for everything from digital art to supply chain tracking to credential verification.
Enhanced User Trust and Transparency
Trust serves as the currency of digital business. Web3 fundamentally changes how companies establish trust. Traditional applications ask users to trust that companies will protect their data, honor their agreements, and operate fairly behind closed doors. In contrast, Web3 dApps replace this need for trust with transparency and verifiability.
The blockchain records every transaction and state change in a dApp. This creates an immutable audit trail that anyone can inspect. Smart contracts operate exactly as developers program them. Therefore, hidden terms or retroactive changes become impossible. This transparency builds user confidence in ways that traditional privacy policies and terms of service never could.
For businesses, this transparency also provides protection. Companies can resolve disputes by examining the blockchain record rather than relying on potentially compromised logs or testimonies. Regulatory compliance becomes easier to demonstrate when the system permanently records and verifies all operations. Moreover, the trust established through blockchain technology can become a significant competitive advantage. This proves particularly valuable in industries where scandals or systemic issues have eroded trust.
Data Ownership and Privacy
The Web 2.0 business model often treats user data as a resource to extract and monetize. Frequently, this happens without meaningful consent or compensation. Web3 inverts this relationship by giving users ownership of their data and identity. Through decentralized identity systems, users control what information they share and with whom. They grant temporary access rather than handing over permanent copies.
This shift has profound implications for digital businesses. Rather than competing to capture and hoard user data, Web3 businesses focus on providing value. This earns users’ willingness to share information. Privacy-preserving technologies like zero-knowledge proofs allow businesses to verify necessary information without accessing the underlying data. Therefore, they enable compliance and security without compromising user privacy.
For businesses concerned about data liability, Web3 offers an attractive alternative. Companies reduce their exposure to data breaches and regulatory penalties by not storing user data centrally. The responsibility for data security shifts partly to users themselves. They hold their own cryptographic keys and control access to their information.
Interoperability and Composability
One of Web3’s most powerful features is the interoperability of dApps and digital assets. Traditional applications exist in walled gardens. Companies lock data and functionality within proprietary systems. Conversely, developers can build Web3 applications on open protocols and standards. This allows them to interact seamlessly with other dApps.
This composability enables rapid innovation. Developers build new applications by combining existing smart contracts and services. It works much like assembling LEGO blocks. For instance, a financial dApp might integrate a decentralized identity service, a payment protocol, and a governance system. Different teams develop all these components, but they work together seamlessly. This reduces development time and creates network effects where each new application adds value to the entire ecosystem.
For businesses, this means access to shared infrastructure and services without vendor lock-in. Integration partnerships that might take months to negotiate in traditional business can happen permissionlessly in Web3. APIs are open and accessible by default, enabling faster collaboration and innovation.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its promise, Web3 dApp development comes with real challenges that businesses must navigate carefully. Blockchain technology continues to evolve. Ongoing debates focus on scalability, energy consumption, and the best approaches to decentralization. User experience in many Web3 applications remains clunky compared to polished Web 2.0 products. Technical concepts like private keys and gas fees create barriers to mainstream adoption.
Regulatory uncertainty looms large over Web3 businesses. Governments worldwide are still determining how to classify and regulate cryptocurrencies, tokens, and decentralized systems. Businesses entering this space must prepare for evolving regulations and potential compliance requirements that don’t yet exist.
The technology also requires different skills and mindsets from development teams. Smart contract programming demands rigorous security practices. Hackers can exploit bugs, and developers find them difficult to fix once deployed. Therefore, businesses must invest in expertise and auditing to ensure their dApps remain secure and reliable.
The Path Forward
Web3 dApp development represents more than a technological upgrade. Instead, it’s a fundamental reimagining of how digital businesses can operate. The combination of transparency, efficiency, user empowerment, and new economic models creates opportunities for innovation. These opportunities were impossible in previous internet eras. While challenges remain, the momentum behind Web3 continues to build. More businesses recognize its potential to solve real problems and create value in new ways.
For forward-thinking businesses, the question isn’t whether to explore Web3. Rather, it’s how to do so strategically. The future of digital business will likely be hybrid. It will combine the best of centralized and decentralized systems. Those who begin building expertise and experimenting with dApp development now will position themselves to lead. As Web3 matures and mainstream adoption accelerates, these early movers will have the advantage they need to succeed in the new digital economy.



